To realize the aspirational purpose of the Paris Settlement on local weather change—limiting the rise in world common floor temperature to 1.5 levels Celsius above preindustrial ranges—would require its 196 signatories to dramatically cut back their greenhouse gasoline (GHG) emissions. These greenhouse gases differ broadly of their world warming potential (GWP), or capacity to soak up radiative power and thereby heat the Earth’s floor.
For instance, measured over a 100-year interval, the GWP of methane is about 28 occasions that of carbon dioxide (CO2), and the GWP of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is 24,300 occasions that of CO2, in response to the Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change (IPCC) Sixth Evaluation Report.
Used primarily in high-voltage electrical switchgear in electrical energy grids, SF6 is without doubt one of the most potent greenhouse gases on Earth. Within the twenty first century, atmospheric concentrations of SF6 have risen sharply together with world electrical energy demand, threatening the world’s efforts to stabilize the local weather.
This heightened demand for electrical energy is especially pronounced in China, which has dominated the enlargement of the worldwide energy business up to now decade. Quantifying China’s contribution to world SF6 emissions—and pinpointing its sources within the nation—could lead on that nation to implement new measures to cut back them, and thereby cut back, if not eradicate, an obstacle to the Paris Settlement’s aspirational purpose.
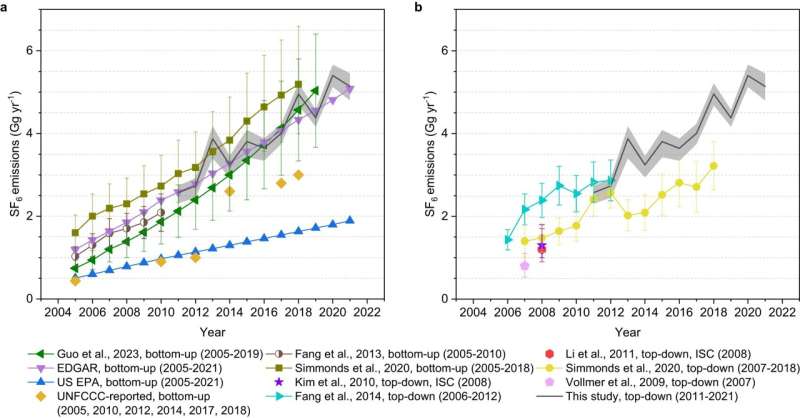
To that finish, a brand new research by researchers on the MIT Joint Program on the Science and Coverage of International Change, Fudan College, Peking College, College of Bristol, and Meteorological Remark Heart of China Meteorological Administration decided whole SF6 emissions in China over 2011-21 from atmospheric observations collected from 9 stations inside a Chinese language community, together with one station from the Superior International Atmospheric Gases Experiment (AGAGE) community.
For comparability, world whole emissions had been decided from 5 globally distributed, comparatively unpolluted “background” AGAGE stations, involving extra researchers from the Scripps Establishment of Oceanography and CSIRO, Australia’s Nationwide Science Company.
The researchers discovered that SF6 emissions in China nearly doubled from 2.6 gigagrams (Gg) per 12 months in 2011, once they accounted for 34 % of world SF6 emissions, to five.1 Gg per 12 months in 2021, once they accounted for 57 % of world whole SF6 emissions. This enhance from China over the 10-year interval—a few of it rising from the nation’s less-populated western areas—was bigger than the worldwide whole SF6 emissions rise, highlighting the significance of decreasing SF6 emissions from China sooner or later.
The open-access research, which seems within the journal Nature Communications, explores prospects for future SF6 emissions discount in China.
“Adopting upkeep practices that reduce SF6 leakage charges or utilizing SF6-free gear or SF6 substitutes within the electrical energy grid will profit greenhouse-gas mitigation in China,” says Minde An, a postdoc on the MIT Heart for International Change Science (CGCS) and the research’s lead creator. “We see our findings as a primary step in quantifying the issue and figuring out how it may be addressed.”
Emissions of SF6 are anticipated to final greater than 1,000 years within the environment, elevating the stakes for policymakers in China and all over the world.
“Any enhance in SF6 emissions this century will successfully alter our planet’s radiative finances—the stability between incoming power from the solar and outgoing power from the Earth—far past the multi-decadal time-frame of present local weather insurance policies,” says MIT Joint Program and CGCS Director Ronald Prinn, a co-author of the research. “So it is crucial that China and all different nations take rapid motion to cut back, and in the end eradicate, their SF6 emissions.”
Extra data:
Minde An et al, Sustained progress of sulfur hexafluoride emissions in China inferred from atmospheric observations, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46084-3
Offered by
Massachusetts Institute of Expertise
This story is republished courtesy of MIT Information (internet.mit.edu/newsoffice/), a preferred website that covers information about MIT analysis, innovation and instructing.
Quotation:
Atmospheric observations in China present rise in emissions of a potent greenhouse gasoline (2024, March 28)
retrieved 28 March 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-03-atmospheric-china-emissions-potent-greenhouse.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.