Researchers on the College of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have proven for the primary time that costly aberration-corrected microscopes are not required to attain record-breaking microscopic decision.
The sphere of microscopy is in the course of an awesome revolution. For the reason that 1800s and the invention of the compound mild microscope, there have solely been a number of main jumps in decision to see completely different size scales: from micro organism and cells, to viruses and proteins, and even right down to single atoms.
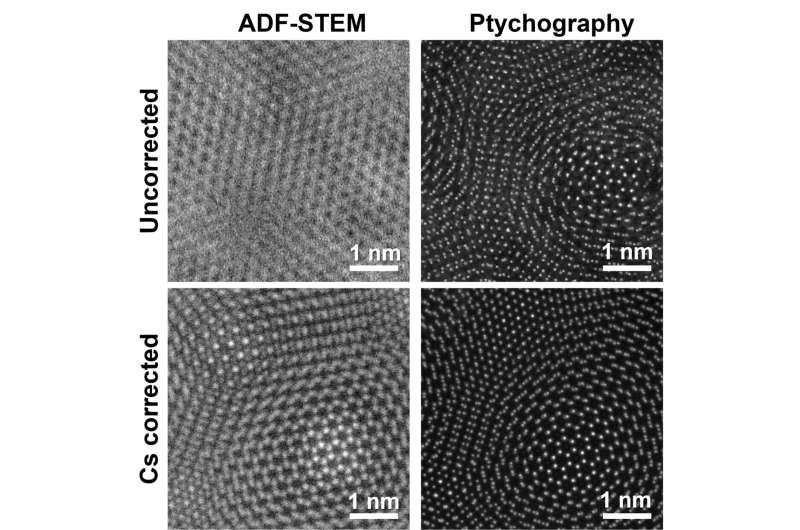
Typically, as decision has been making these unbelievable jumps, so has the worth of the microscopes used to attain that decision. Such hefty value tags severely restrict the accessibility of those devices. The present leap in decision comes from a brand new approach known as electron ptychography—a technique that makes use of computation to spice up the decision of electron microscopes—which has taken the sector by storm within the final 5-6 years.
Researchers on the College of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated record-breaking decision utilizing electron ptychography on “standard” transmission electron microscopes (standard that means with out costly aberration correctors). This breaks the development of accelerating microscope value with growing decision. They have been capable of obtain deep sub-angstrom spatial decision right down to 0.44 angstrom (one angstrom is one ten-billionth of a meter), which exceeds the decision of aberration-corrected instruments and rivals their highest ptychographic resolutions.
“For the final 90-100 years, our area has thought that the way in which to do nice microscopy is to make higher and higher microscopes,” says supplies science & engineering professor Pinshane Huang, who led this work. “Probably the most thrilling factor about our analysis is that we’re exhibiting that you do not want a cutting-edge microscope to make this work. We are able to take a ‘standard’ microscope and do the identical factor, utilizing ptychography, and it is simply nearly as good! That is wonderful as a result of there is usually a multi-million-dollar distinction in value between the 2 setups.”
This analysis, co-first authored by former MatSE UIUC postdoctoral researcher Kayla Nguyen, former MatSE UIUC graduate scholar Chia-Hao Lee and Argonne Nationwide Laboratory employees scientist Yi Jiang, was just lately revealed within the journal Science.
Earlier than ptychography, the very best decision electron microscopes used a know-how known as aberration-correction to permit scientists to see particular person atoms. Quite than utilizing a beam of sunshine to probe a pattern, electron microscopes use a beam of electrons, centered by electromagnets.
Electrons have wavelengths hundreds of occasions smaller than seen mild, which permits electron microscopes to resolve objects which can be many occasions smaller than could be seen with optical microscopes. Scientists use these microscopes to decode the buildings of objects starting from the spike protein on the COVID-19 virus to the preparations of atoms in graphene and, extra usually, to look inside matter to know its atomic construction, composition and bonding.
Nonetheless, one of many challenges of utilizing beams of electrons is focusing that beam. “It is inconceivable to make an ideal lens for electrons,” Huang says. “What folks have been doing to compensate is making ‘unhealthy’ lenses, after which placing aberration correctors after them, that are a sequence of ‘unhealthy’ lenses which can be ‘unhealthy’ in reverse methods. Summed collectively, they make ‘okay’ lenses, and that is been the gold customary for a way we picture on the atomic scale for not less than 20 years.”
In optics, an aberration is any method {that a} lens deviates from an ideal lens. For instance, human eyes can have a number of varieties of aberrations akin to short- and near-sightedness (eyes cannot focus in any respect distances) and astigmatism (curvature of the eyeball that causes blurred imaginative and prescient).
Lee explains, “For electromagnetic lenses, the way in which to focus these electrons is thru an electromagnetic area. However we do not have an effective way of controlling the form and the power of the electromagnetic area, which places a really robust limitation on how exact we could be focusing these electrons.”
In aberration-corrected microscopy, the present cutting-edge know-how, there may be an additional stack of lenses to right the aberrations from the common lenses, that modifications the form of the beam earlier than it hits the pattern. These additional aberration-correcting lenses are the place important prices are added to the microscope.
Whereas it’s inconceivable to make an ideal lens, the objective of the final 100 years has been to constantly make higher lenses to attenuate aberrations. However Huang says, “What’s thrilling about ptychography is that you do not have to make higher and higher lenses. What we will do as an alternative is use computer systems.”
Quite than utilizing a stack of lens optics to take away aberrations, ptychography removes them computationally. With a brand new technology of detectors, known as hybrid pixel detectors, that value a number of hundred thousand {dollars} (in comparison with aberration-corrected microscopes that value as much as $7 million) and pc algorithms, this methodology can double, triple and even quadruple the decision of what a microscope can obtain with its bodily lenses.
Huang and her workforce have proven that their strategy quadruples the decision of standard transmission electron microscopes. Additional, practically any scanning transmission electron microscope can now be tailored to attain state-of-the-art decision at a fraction of the fee.
Whereas this strategy is game-changing, Huang notes that ptychography remains to be a difficult approach that requires a number of computation energy. It could take hours to get a single reconstruction to succeed in the perfect decision. However, as with many different applied sciences, computation advances fairly quickly and will get cheaper, quicker and simpler to make use of.
“We introduced a cutting-edge approach, electron ptychography, to standard transmission electron microscopes to indicate for the primary time {that a} ‘mediocre’ microscope can just do in addition to the most costly microscopes available on the market,” Huang says.
“That is important for the lots of of establishments throughout the nation and internationally who beforehand could not afford the innovative. Now, all they want is a detector, some computer systems and electron ptychography. And when you do this, you’ll be able to see the atomic world with rather more element than anybody imagined even 10 years in the past. This represents an enormous paradigm shift.”
Extra info:
Kayla X. Nguyen et al, Reaching sub-0.5-angstrom–decision ptychography in an uncorrected electron microscope, Science (2024). DOI: 10.1126/science.adl2029
Offered by
College of Illinois Grainger School of Engineering
Quotation:
Reimagining electron microscopy: Bringing high-end decision to lower-cost microscopes (2024, February 26)
retrieved 26 February 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-02-reimagining-electron-microscopy-high-resolution.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.